Understanding the Unilateral Oophorectomy Procedure: Comprehensive Insights from Expert Obstetricians & Gynecologists

The field of women's health and medical care has seen remarkable advancements, with procedures like the unilateral oophorectomy becoming increasingly prevalent. At drseckin.com, top-tier obstetricians and gynecologists are dedicated to providing comprehensive care, guiding women through complex treatment options with expertise and compassion. This article aims to shed light on the unilateral oophorectomy procedure, its indications, execution, benefits, risks, and the crucial role expert medical professionals play in ensuring optimal outcomes. Whether you are a patient seeking knowledge or a healthcare provider looking to deepen your understanding, this detailed guide will help you navigate the intricacies of this surgical intervention.
What Is a Unilateral Oophorectomy?
A unilateral oophorectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the *removal of one ovary* in a woman. The term "unilateral" indicates that only one side is affected, as opposed to a bilateral oophorectomy, which entails removal of both ovaries. This procedure is performed for various medical reasons, ranging from benign cysts to ovarian cancers, and is a vital option in preserving reproductive health whenever possible.
The surgical removal of an ovary does not always compromise a woman's overall hormonal balance, especially if the other ovary remains intact. However, in some cases, the procedure's implications extend beyond immediate health concerns, impacting fertility, hormone production, and overall well-being.
Common Indications for a Unilateral Oophorectomy
The decision to perform a unilateral oophorectomy hinges upon a variety of clinical indications, each warranting careful evaluation by experienced doctors and OB-GYN specialists. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Ovarian Cysts: Large, persistent, or complex ovarian cysts that do not resolve with conservative management may necessitate removal.
- Ovarian Tumors: Benign or malignant tumors detected in one ovary often require surgical intervention to prevent the spread or further complications.
- Endometriomas: Endometriosis involving a single ovary can lead to significant pain or fertility issues, prompting removal.
- Ovarian Torsion: Twisting of the ovary cutting off blood supply often results in the urgent need for removal to preserve health.
- Thrombosis or Infection: Severe infections such as tubo-ovarian abscesses may require surgical excision of the affected ovary.
- Prophylactic Reasons: In high-risk patients, such as those with BRCA mutations, preventive removal of affected ovaries may be considered.
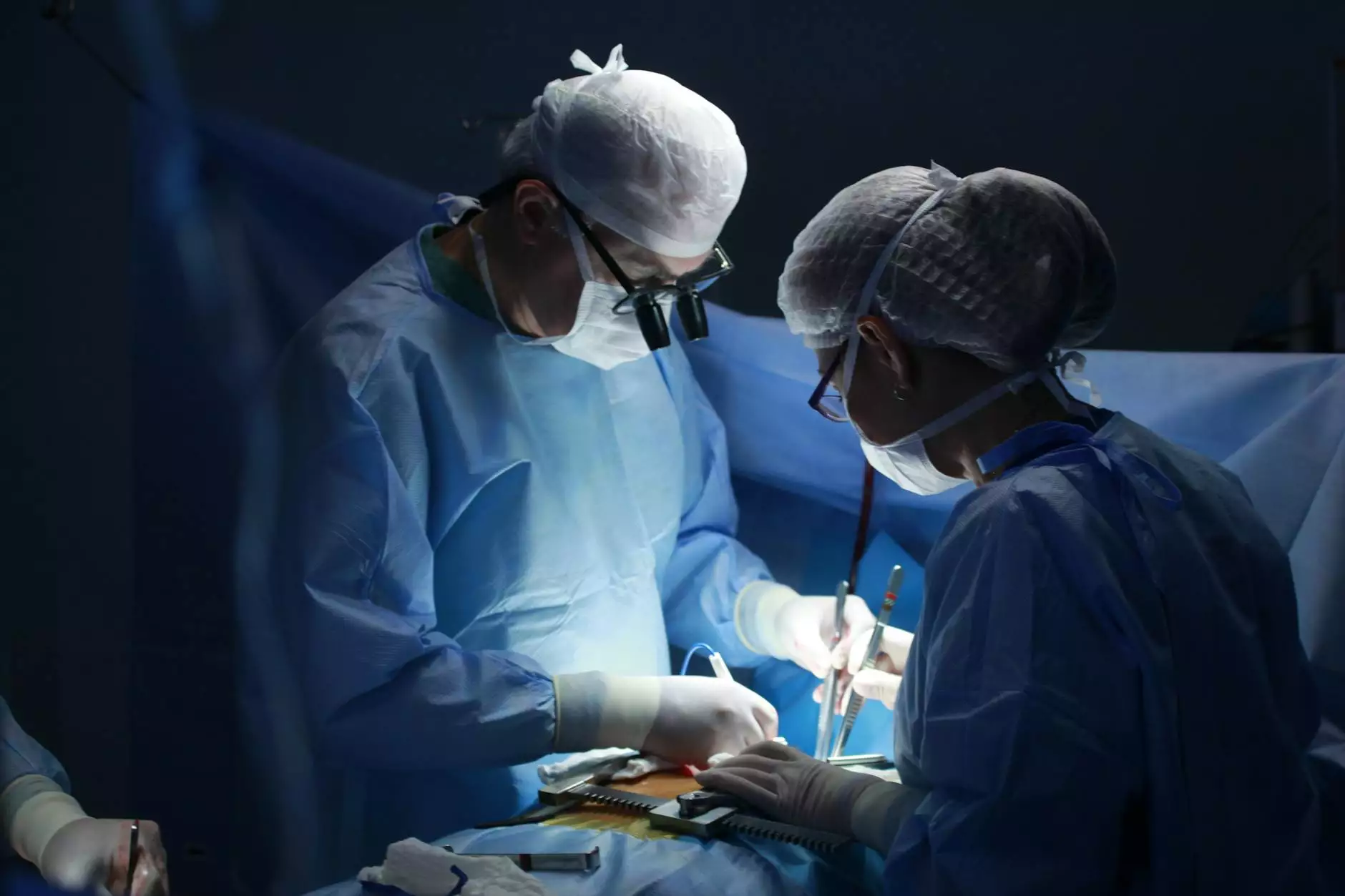
The Surgical Process of the Unilateral Oophorectomy Procedure
The unilateral oophorectomy procedure is a carefully planned surgery performed by expert obstetricians and gynecologists. It can be executed via various methods, with the laparoscopic approach being the most common due to its minimally invasive nature.
Preparation Before Surgery
Prior to the procedure, comprehensive diagnostic assessments including imaging (ultrasound, MRI, CT scans) and blood tests are conducted to confirm the pathology and evaluate overall health. Patients are advised to discuss their medical history, allergies, current medications, and any concerns with their healthcare provider.
The Surgical Technique
The typical steps involved in a unilateral oophorectomy are as follows:
- Anesthesia: Usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and immobilization.
- Access: Using laparoscopy, small incisions are made in the abdomen to facilitate the insertion of a camera and surgical instruments.
- Identification: The affected ovary is carefully located, and surrounding tissues are gently dissected to prevent damage to adjacent organs.
- Removal: The ovary is ligated at its blood vessels and detached from supporting structures, then removed through the incision.
- Closure: The surgical sites are closed, typically with dissolvable sutures or staples, and the patient is moved to recovery.
The minimally invasive approach reduces postoperative pain, minimizes scarring, and shortens hospital stays. In certain complex cases or large tumors, an open surgery (laparotomy) may be indicated.
Benefits of the Unilateral Oophorectomy
The unilateral oophorectomy offers numerous advantages when performed by seasoned Doctors, Health & Medical professionals:
- Effective treatment of ovarian pathology: Removal of diseased or at-risk tissue prevents malignancy progression.
- Preservation of fertility: Since only one ovary is removed, many women retain their reproductive potential.
- Reduced hormonal disruption: The remaining ovary continues hormone production, helping maintain hormonal balance.
- Minimized surgical trauma: Minimally invasive techniques reduce recovery time and postoperative discomfort.
- Decreased risk of recurring issues: Removing problematic tissue reduces the chances of cyst or tumor recurrence on that side.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any surgery, the unilateral oophorectomy procedure carries certain risks, which are minimized when performed by experienced obstetricians & gynecologists. These include:
- Bleeding: Excessive intraoperative or postoperative bleeding.
- Infection: Surgical site infections, which can be managed with antibiotics.
- Damage to adjacent organs: Such as the bladder or intestines, though rare with expert surgeons.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Usually minimal with a healthy remaining ovary, but in some cases, early menopause symptoms may occur.
- Avoidable complications: Including blood clots, anesthetic reactions, or adhesion formation.
It is essential that patients discuss these potential risks thoroughly with their healthcare team and adhere to pre- and post-operative instructions to ensure a smooth recovery.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Recovery from a unilateral oophorectomy is generally swift, especially when performed laparoscopically. Patients can expect:
- Hospital stay: Usually 1–2 days for minimally invasive surgery.
- Activity restrictions: Light activity for several days; avoid strenuous exercise for 2–4 weeks.
- Pain management: Mild discomfort is common and can be controlled with prescribed medications.
- Follow-up appointments: Critical for monitoring healing and addressing concerns.
- Monitoring hormonal function: Especially if the remaining ovary or hormone levels are a concern.
Importance of Choosing Expert Obstetricians & Gynecologists
The success of a unilateral oophorectomy heavily relies on the skill and experience of the Doctors, Health & Medical specialists involved. Reputable clinics like drseckin.com are known for their comprehensive, patient-centered care, utilizing state-of-the-art technology and evidence-based practices. A meticulous approach by specialists ensures:
- Accurate diagnosis and tailored surgical plans
- Minimization of risks and complications
- Effective pain management and speedy recovery
- Postoperative support and counseling
- Ongoing care for hormonal and reproductive health
Conclusion: Embracing Advanced Women’s Healthcare
The unilateral oophorectomy procedure exemplifies how modern Women’s health and medical specialties continue to evolve, offering women safe, effective, and minimally invasive options to address various ovarian conditions. When performed by top-tier obstetricians and gynecologists, patients can expect excellent outcomes, preserving their health, fertility, and quality of life.
As part of a comprehensive healthcare approach, understanding this operation empowers women to make informed decisions and seek the care they deserve. For personalized consultations and expert surgical interventions, trust the dedicated professionals at drseckin.com. Your journey to optimal reproductive health begins with expert guidance and compassionate care.